5 Assays for the determination of IgG subclass levels
Different methods are in use for the quantitative determination of IgG subclasses. For most methods, The Central Laboratory of the Netherlands Red Cross Blood Transfusion Service (CLB) is a manufacturer of special reagents and kits:
5.1 Radial Immunodiffusion (RID)
RID (Mancini) is a classical diagnostic method to determine IgG subclasses. This reliable assay is widely used and easy to perform. However, when large numbers of samples have to be processed the relatively long incubation times will be a disadvantage.
Brief outline of the method:
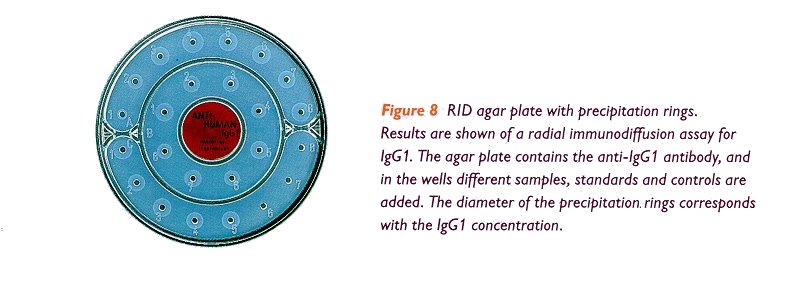
The RID assay is performed in (ready-for-use) agar plates, containing the specific
anti-IgG subclass antibodies (figure 8). Test samples, standard-and control
sera are prepared and added to the plates. After 48-64 hours incubation at room
temperature the diameters of the immunoprecipitation rings are measured. The
IgG subclass concentrations in the test samples may be quantified in two ways:
a) Calibration curve method: ring diameters and concentrations of the standards
are plotted and the values of the test sample are determined by interpolation.
b) Tabular method: ring diameters of the calibration curve are listed and the
values of the test sample are read from a table. It is not necessary to make
a calibration curve. The control serum is assayed to check the validity of the
calibration curves and also the accuracy of the IgG subclass quantification,
when using the table.

5.2 Nephelometry and turbidimetry
The nephelometric quantification is based upon the specific reaction of a monospecific anti-IgG subclass-specific antiserum with the human IgG subclass to be determined. The generated immune complexes are quantified by measuring the side-scattered light. A distinct advantage of nephelometry is the relatively short incubation time. As another advantage, nephelometry assays may be readily automated and are therefore suitable for the routine measurement of IgG subclasses in large numbers of samples.
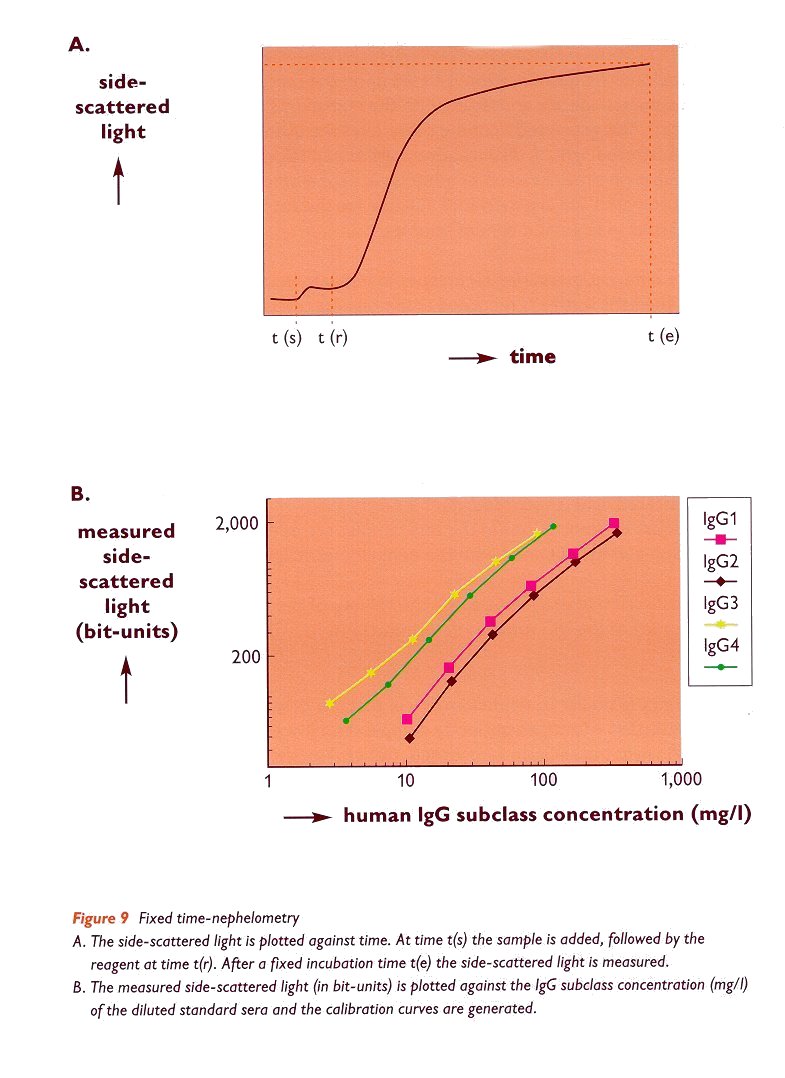
Fixed time-nephelometry is illustrated in figure 9.
Brief outline of the method:
-Diluted samples (serum, plasma or other biological fluids), standard-and control
sera are introduced in the reaction tubes of the nephelometer;
-Appropriate anti-IgG subclass reagents and reaction buffer are added;
-Side-scattered light is recorded;
-IgG subclass concentrations in the test samples are calculated relative to
the calibration curves, obtained with the nephelometric IgG subclass standard
serum;
-A control serum is assayed to check the validity of the calibration curves
and the accuracy of the IgG subclass determinations.
Turbidimetry is similar to nephelometry in that it is based upon the fluid-phase optical detection of antigen complexes. However, in turbidimetry the decrease in light transmission is recorded, rather than the side-scattered light, which is measured in nephelometry.