<-- Home
Strings of data can be transferred between
computers by wire or by air.
Serial communication is an long proven solid method
to send small amounts of data, like instructions or records from measurement on
a remote device.
An universal asynchronous
receiver-transmitter (UART) is a computer hardware device for asynchronous
serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are
configurable as Wikipedia describes it.
The serial port on a PC can be connected by wire to an
other PC's serial port.
If from both wires the TX (transmit) pin from one PC is connected
to the RX (receive) pin of the other PC, the PC's can communicate.
Both PC's must be set to the same transmission speed, the baud rate. The baud
rate is how many bits per second are send over the wires.
A standard communication speed is 9600 baud = 9600 bits
per second. In this string of bits
some are control bits. 9600 baud is roughly 1000 bytes per second.
A baud rate of
115200 is also a common used speed.
There are several methods that can be used to send
data through the air.
ESP32 and some Arduino MCU's use the Nordic nRF52 chipsets. They are often
integrated in the processor boards together with an WIFI module.
Bluetooth has a range of 10 meters and can be transmitted and received with a
mobile phone.
There are similar serial radio modules, known as HC-12, that has ranges up to 1000
meter. (See an
example here)
Two HC-12 modules can be used instead of a long cable between two devices. They
are easy to operate but you can not use a phone.
A HM-10 or similar BLE module, like JDY-23, can be used with Android and Apple
phones. HC-0x modules, like the popular HC-05, can not be used with Apple
devices. Therefore HM-10 modules are a good choice.
This page describes how to use a phone to communicate with an ESP32 program to send instructions and receive results.
For the more detailed version see the Instructable of this page
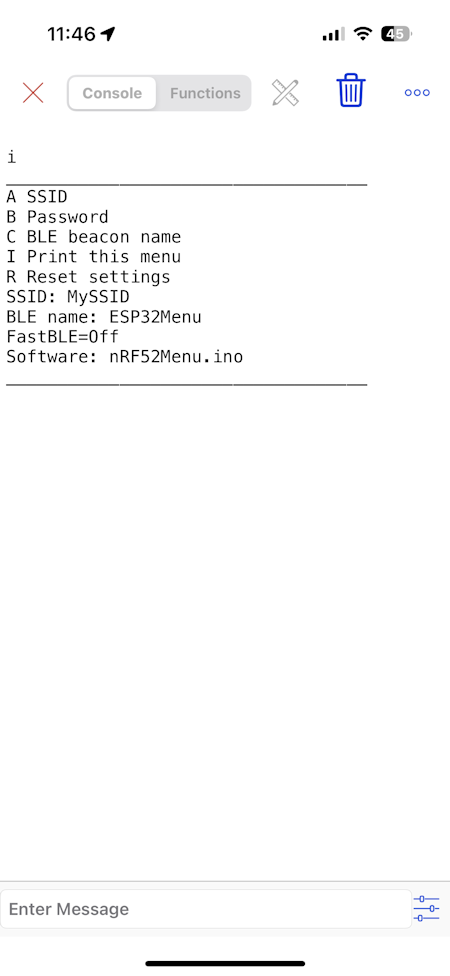
The menu to display in the terminal

The menu is a character array with text to be displayed.
In this example a menu line can not be longer than 40 characters.
When you send the character i the menu is displayed in the app.
//--------------------------------------------
// Menu
//0 1 2 3 4
//1234567890123456789012345678901234567890----
char menu[][40] =
{
"A SSID",
"B Password",
"C BLE beacon name",
"I Print this menu",
"R Reset settings"
};
The subroutine below translates the received command line to an action;a subroutine to be executed.
//--------------------------------------------
// CLOCK Input from Bluetooth or Serial
//--------------------------------------------
void ReworkInputString(String InputString)
{
char ff[50]; InputString.toCharArray(ff,InputString.length()); // Convert a String to char array
sprintf(sptext,"Inputstring: %s Lengte : %d\n", ff,InputString.length()-1);
// Tekstprint(sptext);
if(InputString.length()> 40){Serial.printf("Input string too long (max40)\n"); return;} // If garbage return
sptext[0] = 0; // Empty the sptext string
if(InputString[0] > 31 && InputString[0] <127) // Does the string start with a letter?
{
switch (InputString[0])
{
case 'A':
case 'a':
if (InputString.length() >5 )
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(Mem.Ssid,InputString.length()-1);
sprintf(sptext,"SSID set: %s", Mem.Ssid);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Use between 4 and 30 characters ****");
break;
case 'B':
case 'b':
if (InputString.length() >5 )
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(Mem.Password,InputString.length()-1);
sprintf(sptext,"Password set: %s\n Enter @ to reset ESP32 and connect to WIFI and NTP", Mem.Password);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"%s,**** Length fault. Use between 4 and 40 characters ****",Mem.Password);
break;
case 'C':
case 'c':
if (InputString.length() >5 )
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(Mem.BLEbroadcastName,InputString.length()-1);
sprintf(sptext,"BLE broadcast name set: %s", Mem.BLEbroadcastName);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Use between 4 and 30 characters ****");
break;
case 'I':
case 'i':
SWversion();
break;
case 'R':
case 'r':
if (InputString.length() == 2)
{
Reset();
sprintf(sptext,"\nReset to default values: Done");
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Enter R ****");
break;
default: break;
}
}
Tekstprintln(sptext);
StoreStructInFlashMemory();
InputString = "";
}
The priced app BLEserial Pro app
has more capabilities and connect to both CC25xx and nRF chipsets.
The NIMBLE library has been upgraded to version 2.
If you still use version 1 then use this
page that has the sketch for the old library
/*
Author : Ed Nieuwenhuijs https://github.com/ednieuw , https://ednieuw.nl
December 2024
Sketch for Bluetooth UART (universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter) communication with a BLE serial terminal.
A serial terminal can be installed on a PC (like Termite) or on a IOS or Android device
For IOS: BLESerial nRF or BLEserial Pro
For Android: Serial Bluetooth Terminal
In this example entries in the serial terminal can be used to set an SSID, password and BLE broadcast name.
******
Compile with NimBLE version 2.n.n
******
In NimBLE version 2.x.x these are the differences:
void onConnect(NimBLEServer* pServer, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo) override {deviceConnected = true;Serial.println("Connected" ); };
void onDisconnect(NimBLEServer* pServer, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo, int reason) override {deviceConnected = false;Serial.println("NOT Connected" );}
void onWrite(NimBLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo) override { std::string rxValue = pCharacteristic->getValue(); ReceivedMessageBLE = rxValue + "\n"; }
add pAdvertising->setName(BLEbroadcastName); after pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(SERVICE_UUID);
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include <NimBLEDevice.h>
//-------------------------------------------- //
// BLE //#include <NimBLEDevice.h>
//--------------------------------------------
BLEServer *pServer = NULL;
BLECharacteristic * pTxCharacteristic;
bool deviceConnected = false;
bool oldDeviceConnected = false;
std::string ReceivedMessageBLE;
#define SERVICE_UUID "6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E" // UART service UUID
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX "6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX "6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
//----------------------------------------
// Common
//----------------------------------------
#define MAXTEXT 255
char sptext[MAXTEXT];
bool UseBLELongString = false;
char SSID[30]; //
char Password[40]; //
char BLEbroadcastName[30]; // Name of the BLE beacon
//----------------------------------------
// Setup
//----------------------------------------
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200); // Setup the serial port to 115200 baud //
int32_t Tick = millis();
while (!Serial)
{if ((millis() - Tick) >5000) break;} Tekstprintln("Serial started"); // Wait max 5 seconds until serial port is started
strcpy(SSID,""); // Default SSID
strcpy(Password,""); // Default password
strcpy(BLEbroadcastName,"Edsoft");
StartBLEService(); Tekstprintln("BLE started"); // Start BLE service
}
//----------------------------------------
// Loop
//----------------------------------------
void loop()
{
CheckDevices();
}
//-------------------------------------------- //
// COMMON Check connected input devices
//--------------------------------------------
void CheckDevices(void)
{
CheckBLE(); // Something with BLE to do?
SerialCheck(); // Check serial port every second
}
//-------------------------------------------- //
// COMMON check for serial input
//--------------------------------------------
void SerialCheck(void)
{
String SerialString;
while (Serial.available())
{
char c = Serial.read(); // Serial.write(c);
if (c>31 && c<128) SerialString += c; // Allow input from Space - Del
else c = 0; // Delete a CR
}
if (SerialString.length()>0)
{
ReworkInputString(SerialString); // Rework ReworkInputString();
SerialString = "";
}
}
//-------------------------------------------- //
// COMMON common print routines
//--------------------------------------------
void Tekstprint(char const *tekst) { if(Serial) Serial.print(tekst); SendMessageBLE(tekst); sptext[0]=0; }
void Tekstprintln(char const *tekst) { sprintf(sptext,"%s\n",tekst); Tekstprint(sptext); }
void TekstSprint(char const *tekst) { Serial.print(tekst); sptext[0]=0;} // printing for Debugging purposes in serial monitor
void TekstSprintln(char const *tekst) { sprintf(sptext,"%s\n",tekst); TekstSprint(sptext); }
//-------------------------------------------- //
// COMMON Input from Bluetooth or Serial
//--------------------------------------------
void ReworkInputString(String InputString)
{
if(InputString.length()> 40){Serial.printf("Input string too long (max40)\n"); return;} // If garbage return
for (int n=0; n<InputString.length()+1; n++) // remove CR and LF
if (InputString[n] == 10 || InputString[n]==13) InputString.remove(n,1);
sptext[0] = 0; // Empty the sptext string
if(InputString[0] > 31 && InputString[0] <127) // Does the string start with a letter?
{
switch (InputString[0])
{
case 'A':
case 'a':
if (InputString.length() >4 && InputString.length() <30)
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(SSID,InputString.length());
sprintf(sptext,"SSID set: %s", SSID);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Use between 4 and 30 characters ****");
break;
case 'B':
case 'b':
if (InputString.length() >4 && InputString.length() <40)
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(Password,InputString.length());
sprintf(sptext,"Password set: %s\n Enter @ to reset ESP32 and connect to WIFI and NTP\n WIFI and NTP are turned ON", Password);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Use between 5 and 40 characters ****");
break;
case 'C':
case 'c':
if (InputString.length() >4 && InputString.length() <30)
{
InputString.substring(1).toCharArray(BLEbroadcastName,InputString.length());
sprintf(sptext,"BLE broadcast name set: %s", BLEbroadcastName);
}
else sprintf(sptext,"**** Length fault. Use between 4 and 30 characters ****");
break;
default: break;
}
}
Tekstprintln(sptext);
InputString = "";
}
// ********************** NimBLE code ************************************
//-----------------------------
// BLE CheckBLE
//------------------------------
void CheckBLE(void)
{
if(!deviceConnected && oldDeviceConnected) // Disconnecting
{
delay(300); // Give the bluetooth stack the chance to get things ready
pServer->startAdvertising(); // Restart advertising
TekstSprint("Start advertising\n");
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
if(deviceConnected && !oldDeviceConnected) // Connecting
{
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
if(ReceivedMessageBLE.length()>0)
{
SendMessageBLE(ReceivedMessageBLE);
String BLEtext = ReceivedMessageBLE.c_str();
ReceivedMessageBLE = "";
ReworkInputString(BLEtext);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------- //
// BLE
// SendMessage by BLE Slow in packets of 20 chars
// or fast in one long string.
// Fast can be used in IOS app BLESerial Pro
//------------------------------
void SendMessageBLE(std::string Message)
{
if(deviceConnected)
{
if (UseBLELongString) // If Fast transmission (for Apple IOS) is possible
{
pTxCharacteristic->setValue(Message);
pTxCharacteristic->notify();
delay(10); // Bluetooth stack will go into congestion, if too many packets are sent
}
else // Packets of max 20 bytes
{
int parts = (Message.length()/20) + 1;
for(int n=0;n<parts;n++)
{
pTxCharacteristic->setValue(Message.substr(n*20, 20));
pTxCharacteristic->notify();
delay(10); // Bluetooth stack will go into congestion, if too many packets are sent
}
}
}
}
//-------------------------------------------- //
// BLE Start BLE Classes NimBLE Version 2.x.x
//------------------------------
class MyServerCallbacks: public NimBLEServerCallbacks
{
void onConnect(NimBLEServer* pServer, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo) override
{deviceConnected = true; Serial.println("Connected" ); };
void onDisconnect(NimBLEServer* pServer, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo, int reason) override
{deviceConnected = false; Serial.println("NOT Connected" );}
};
class MyCallbacks: public NimBLECharacteristicCallbacks
{
void onWrite(NimBLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic, NimBLEConnInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::string rxValue = pCharacteristic->getValue();
ReceivedMessageBLE = rxValue + "\n";
// if (rxValue.length() > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < rxValue.length(); i++) printf("%c",rxValue[i]); }
// printf("\n");
}
};
//-------------------------------------------- //
// BLE Start BLE Service
//------------------------------
void StartBLEService(void)
{
BLEDevice::init(BLEbroadcastName); // Create the BLE Device
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer(); // Create the BLE Server
pServer->setCallbacks(new MyServerCallbacks());
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID); // Create the BLE Service
pTxCharacteristic = // Create a BLE Characteristic
pService->createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX, NIMBLE_PROPERTY::NOTIFY);
BLECharacteristic * pRxCharacteristic =
pService->createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX, NIMBLE_PROPERTY::WRITE);
pRxCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks());
pService->start();
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = BLEDevice::getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(SERVICE_UUID);
pAdvertising->setName(BLEbroadcastName);
pServer->start(); // Start the server Nodig??
pServer->getAdvertising()->start(); // Start advertising
TekstSprint("BLE Waiting a client connection to notify ...\n");
}